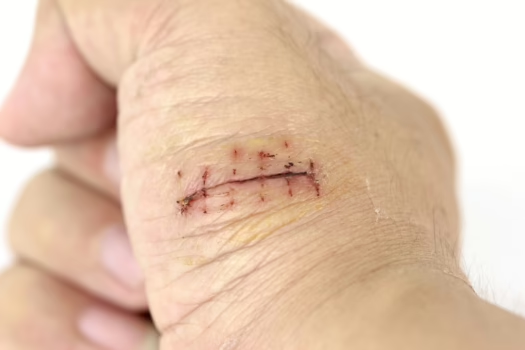
Most cuts and scrapes heal on their own with basic first aid care. However, some wounds need professional medical attention to heal properly and prevent complications. Certain types of injuries require stitches to close the wound safely and reduce the risk of infection or permanent scarring.
Several factors determine whether a wound needs stitches or other medical treatment. The depth of the cut, its location on the body, and how long the edges stay open all play important roles in this decision. Understanding these key differences helps people know whether they should treat a wound at home or seek immediate medical care. This knowledge can prevent serious complications and promote faster recovery.
Deep cuts that penetrate through the skin layers
Deep lacerations slice through multiple layers of skin. They often reach the dermis, fat tissue, or muscle beneath the surface. These wounds typically result from sharp objects like knives, broken glass, or machinery. The cuts appear wide and may expose underlying tissues. Deep cuts usually bleed heavily due to damaged blood vessels. The edges of the wound often pull apart, especially in areas with frequent movement like joints. Medical professionals need to examine these injuries promptly. Deep wounds require cleaning to prevent infection and proper closure techniques.
Stitches help bring the wound edges together for proper healing. They also reduce scarring and protect internal structures from exposure. Services for urgent care and wound stitching can treat many deep cuts effectively. However, extremely deep wounds may need emergency room care. The depth determines the treatment approach. Cuts that reach muscle, tendons, or bone need immediate medical attention for proper repair.
Wounds with jagged or uneven edges
Jagged wounds have rough, uneven edges that do not line up neatly. These cuts happen from forceful tears or contact with dull objects. The irregular shape makes it hard for the skin to heal properly on its own.
Sharp objects can also create jagged wounds if they cut at an angle. Broken glass, torn metal, or accidents often cause this type of injury. The uneven edges cannot close together smoothly without help.
Medical professionals recommend stitches for most jagged wounds. The stitches pull the irregular edges together and help them heal evenly. This reduces the chance of infection and scarring.
Jagged cuts also take longer to heal than clean, straight cuts. The body has more work to do to repair the uneven tissue. However, proper medical care helps speed up recovery.
People should seek medical attention for any cut with rough or torn edges. A doctor can clean the wound properly and decide if stitches are needed. Quick treatment leads to better results and less scarring.
Cuts longer than half an inch
Cuts that measure more than half an inch in length typically require medical attention and stitches. These wounds are too large to heal properly on their own.
The body struggles to close gaps this size naturally. Without proper closure, the wound edges remain separated and take much longer to heal.
Longer cuts also carry a higher risk of infection. Bacteria can easily enter the open wound and cause complications.
These wounds often leave more noticeable scars if left untreated. Stitches help bring the skin edges together for better cosmetic results.
Medical professionals can properly clean and close these cuts. They will assess the depth and location to determine the best treatment approach.
People should seek medical care promptly for cuts exceeding half an inch. Quick treatment leads to better outcomes and faster recovery times.
Injuries where bleeding does not stop after 10 minutes
Cuts that continue to bleed after 10 minutes of direct pressure almost always need medical care. This extended bleed time indicates the wound is deeper than it first appears.
Apply firm pressure with a clean cloth or gauze pad for a full 10 to 15 minutes. However, if blood still flows freely after this time, the person should seek immediate medical attention.
Blood that spurts from a wound signals a cut artery. This type of injury requires emergency care right away. Therefore, call for help immediately if you notice spurts of blood.
Deep wounds often damage blood vessels beneath the skin. As a result, they cannot stop the flow of blood on their own. Medical professionals can close these wounds with stitches to control the loss of blood.
Never ignore persistent flow of blood from any cut. In addition, wounds on the neck, chest, or stomach that continue to bleed need emergency room care rather than urgent care visits.
Facial wounds that might cause noticeable scarring
Facial cuts can leave permanent scars if they do not heal properly. The face has delicate skin that shows marks more easily than other body parts.
Jagged or irregular cuts on the face create uneven edges. These wounds heal poorly without stitches and often result in raised or wide scars.
Cuts to the eyelids need special attention. Even small cuts in this area can affect how the eye looks and functions. Deep eyelid wounds may impair vision if left untreated.
Lip injuries require careful treatment to prevent visible scars. Cuts that go through the lip border create noticeable differences in the lip's shape and outline. These wounds need stitches to keep both sides even.
Deep cuts that go through multiple skin layers leave larger scars. The deeper the wound, the more likely it will create a permanent mark on the face.
Medical treatment works best within eight hours of the injury. Quick care reduces the chance of infection and helps wounds heal with less scarring.
Conclusion
Proper wound assessment saves time and prevents complications. Deep cuts that gape open, expose fat or muscle, or bleed heavily need medical attention within 6 to 8 hours.
People should seek stitches for wounds longer than half an inch or deeper than a quarter inch. Location matters too – cuts on joints, hands, face, or genitals require professional care.
Simple cuts that stop bleeding with pressure and have clean edges can heal at home with basic first aid. However, any doubt about wound severity means a trip to urgent care or the emergency room is the safer choice.
Follow me down the rabbit hole!
I'm Alice and I live with a dizzying assortment of invisible disabilities, including ADHD and fibromyalgia. I write to raise awareness and end the stigma surrounding mental and chronic illnesses of all kinds.